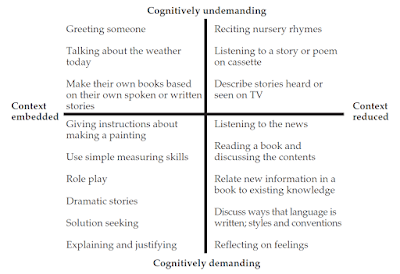
BIC = Basic interpersonal communciation. This includes organisational language such as commands and use of the imperative or simple questions. It also includes insructions.
CALP = Cognitive academic language proficiency. Using language that involves reflection, evaluation and analysis. High ordeer thinking skills.
Second language aquisition - essential information
"Sensitivity to the need for context support and the cognitive demands of a classroom are important if an individual is to maximise learning in the curriculum"
Baker (2001:180)
Cummins' iceberg comparison. Above the surface are language skills such as comprehension and speaking. Underneath the surface are the skills of analysis and synthesis. Above the surface are the language skills of pronunciation, vocabulary and grammar. Below the surface are the deeper, subtle language skills of meanings and creative composition.
Context embedded communication (Good degree of support in communication, particularly via body language.)
Context reduced communication (Very few cues to the meaning that is being transmitted. The words of the sentence exist almost alone in conveying the meaning.)
Colin Baker (2001:176)
Regarding inclusion and how we percieve the world and people in it, I found this section really interesting:
"We make sense of our world by continual classification. People are constantly compared and contrasted. Yet the simplification of categorization often hides the complexity of reality. Sorting often simplifies unsympathetically. Individual differences are reduced to similarities. Yet over-complexity can be unwelcome and confusing. Complications can confound those needing order and pattern. The measurement of bilinguals attempts to locate similarities, order and pattern."
Baker (2001:18)
KEY POINTS FROM Chapter 8
• Two languages acting like a balance in the thinking quarters of a bilingual is incorrect. Instead the Common Underlying Proficiency model suggests that languages operate from the same central operating system.
• The Thresholds Theory suggests that bilinguals who have age-appropriate competence in both languages share cognitive advantages over monolinguals.
• There is a distinction between Basic Interpersonal Communicative Skills (BICS) that concern everyday, straightforward communication skills that are helped by contextual supports, and Cognitive/Academic Language Proficiency (CALP). CALP is the level of language required to understand academically demanding subject matter in a classroom. Such language is often abstract, without contextual supports such as gestures and the viewing of objects.
• On average, it takes about two years for a new immigrant to acquire Basic Interpersonal Communicative Skills in a second language, but five to eight years to achieve Cognitive/Academic Language Proficiency in that second language.
Colin Baker (2001) Foundations of Bilingual Education and Bilingualism, Multilingual Matters.



No comments:
Post a Comment